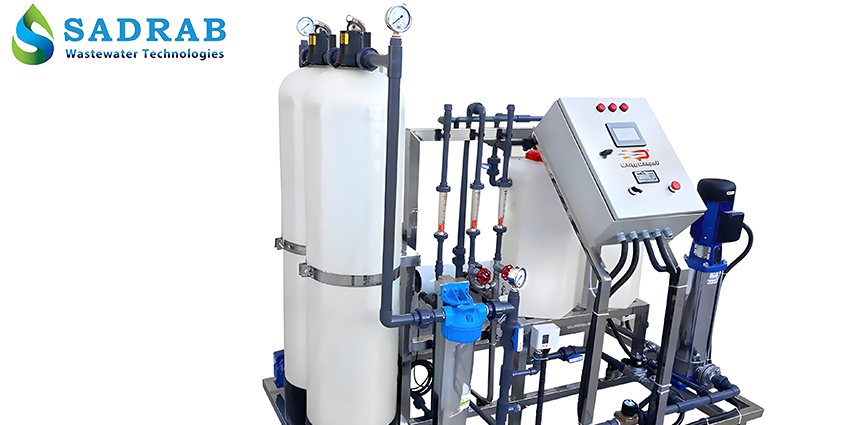
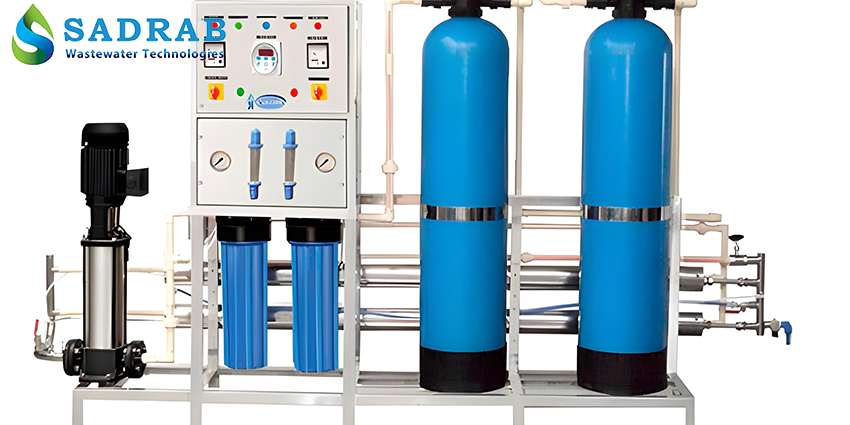
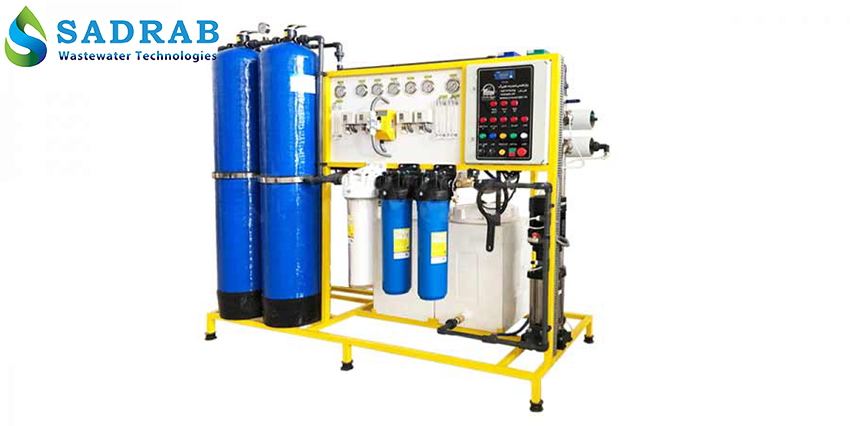
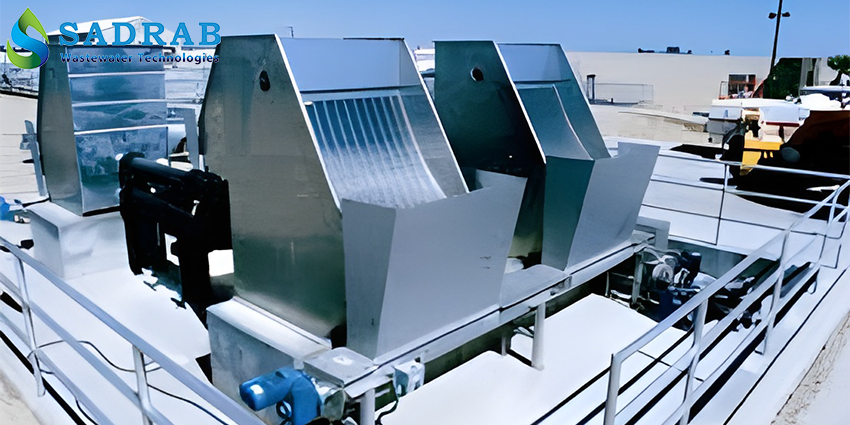
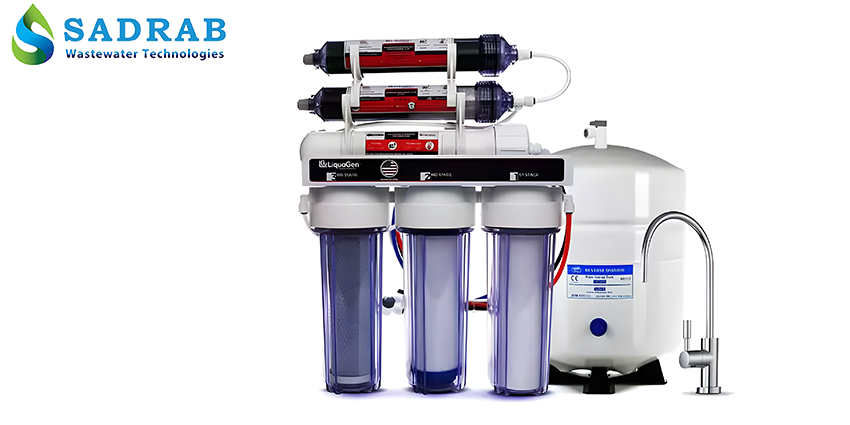
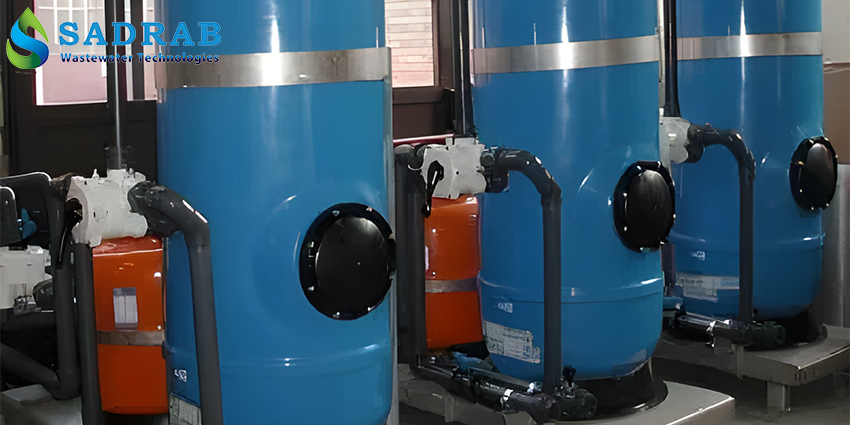
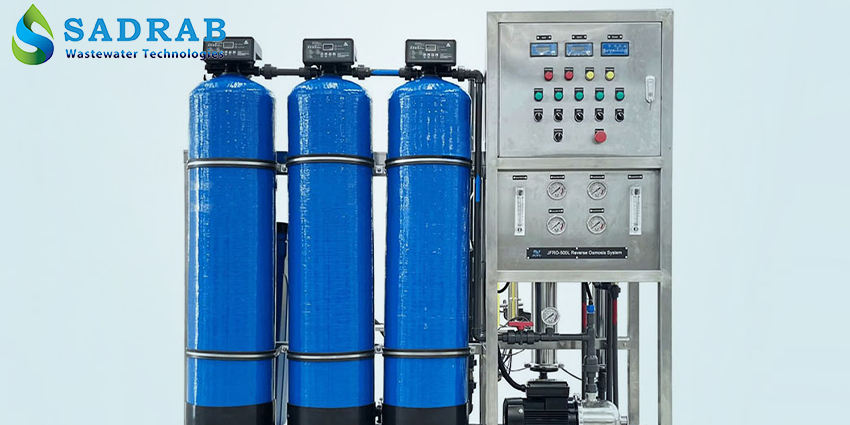
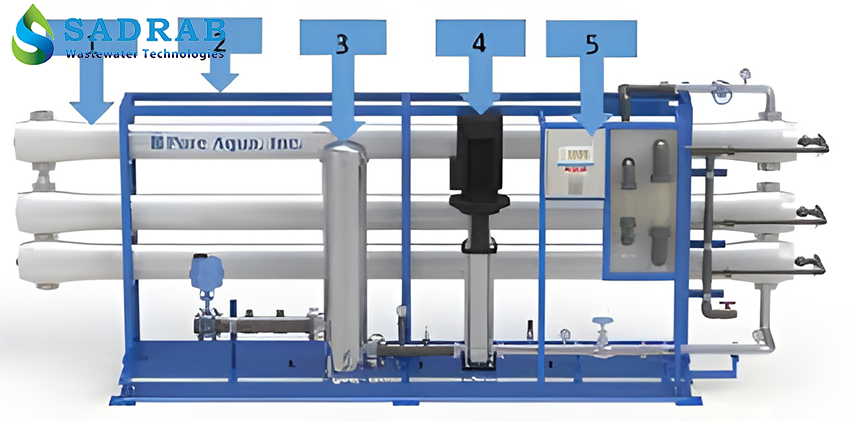
Industrial RO System
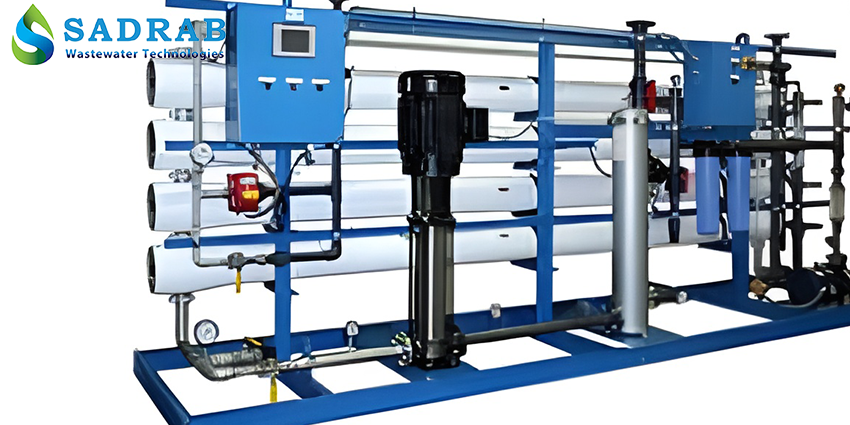

Features of Industrial RO System:
- Custom-built based on water analysis and consumption capacity
- Equipped with pre-treatment units, including sand, carbon, and micron filters
- Uses high-pressure pumps from leading European brands
- Fitted with precision instruments and PLC for intelligent process control
- Includes a CIP (Chemical Cleaning) system for membrane maintenance
- Capable of reducing EC and TDS to below 10 µS/cm
- Portable or skid-mounted design for easy transportation
- After-sales service and spare parts supply available throughout Iran

Support Services and Expert Consultation

Customized Solutions for Clients

Guaranteed Product Quality and Performance

Expertise in Wastewater Treatment Technologies
Additional Information
Industrial Desalination (Reverse Osmosis System) – Sadrab Caspian Purification
Pure and high-quality water is extremely important in industry because impurities can cause equipment corrosion, efficiency loss, and reduced product quality. Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are one of the advanced and widely used industrial water treatment methods, capable of removing a broad range of contaminants including salts, metals, and microorganisms. In summary, the industrial desalination system operates by applying pressure to the feed water to pass pure water molecules through semi-permeable membranes, separating the concentrated salts.
Definition and Operation of Industrial RO Unit
The industrial RO unit directs water using a high-pressure pump, applying pressure higher than the osmotic pressure into a chamber containing a semi-permeable membrane. In this process, almost only pure water molecules can pass through the very fine pores of the membrane; therefore, on one side of the tank, high-purity output water is produced, and on the other side, concentrated water containing impurities (brine) is generated. The pore size of the RO membrane is even smaller than the size of viruses and bacteria; thus, almost all dissolved solids and microorganisms are removed.
Note: The applied pressure must exceed the osmotic pressure of the feed water solution to reverse the natural osmotic flow.
Exclusive Features of Sadrab Caspian Purification Units
Build Quality and Standards: Design and manufacturing of all mechanical and electronic components are done according to international standards using high-quality materials.
Advanced Membrane Selection: Use of high-quality semi-permeable membranes (RO) capable of complete removal of heavy metals and microorganisms.
Support and After-Sales Service: Providing parts replacement warranty, periodic maintenance services, and free technical consultation to ensure optimal device performance.
Flexibility in Capacity and Scale: Modular system options available with varying capacities based on customer needs (from a few cubic meters up to hundreds of cubic meters per day).
Automated Management: Utilizing advanced controllers and programmable logic controllers (PLC) for intelligent control of key system parameters and operational data logging.
What is an Industrial Distillation Unit?
Technologies and Components Used in Industrial RO Systems
Industrial RO units typically include the following components:
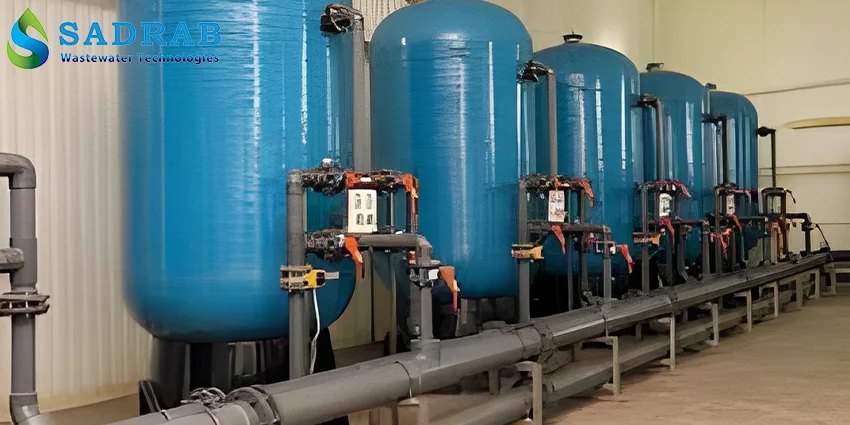
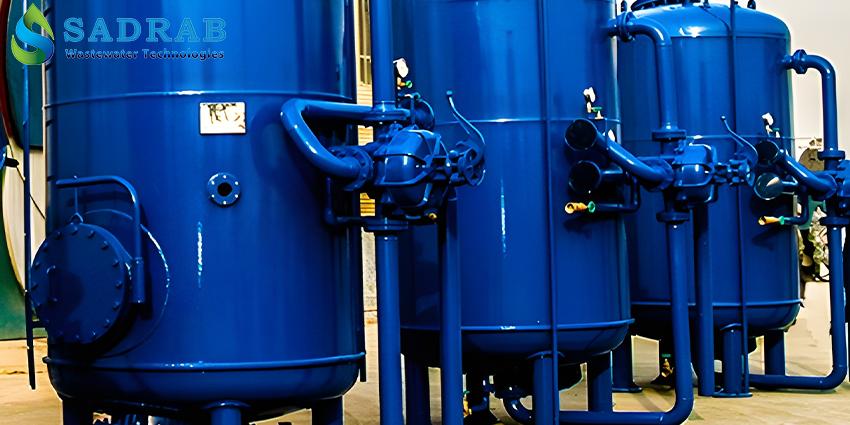
Pre-treatment System: Includes sand filters, carbon filters, and cartridge filters to remove suspended particles and chlorine from the feed water. Proper pre-treatment helps reduce membrane fouling and extends its lifespan.
Industrial Sand Filter (shown above): An example of pre-treatment equipment that removes suspended solids.
High-Pressure Pump: Responsible for providing the necessary pressure to push water through the membrane. RO high-power pumps generate very high pressure so that the feed water passes through the membrane forcefully. These pumps must be designed for high efficiency and appropriate energy consumption.
Semi-Permeable Membrane: The heart of the RO system, responsible for molecular separation. Industrial RO membranes can remove more than 98–99% of total dissolved solids (TDS) and heavy metals. Due to membrane sensitivity, feed water quality control and prevention of fouling are critically important.
Controller and Instrumentation: Includes electrical conductivity (EC) meters, hardness meters, temperature displays, and PLCs for automatic process programming and control. These controllers display key parameters like flow rate and water quality in real-time and allow for automatic adjustments.
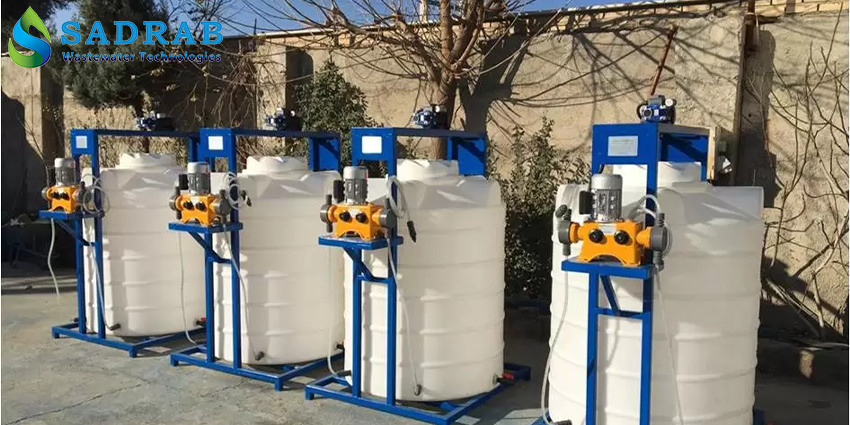
Chemical Injection (Anti-scalant, etc.): To prevent mineral scaling on the membrane, anti-scalant solution is injected into the feed water. Anti-scalants are key chemicals in RO systems that prevent calcium and sulfate deposits. Additionally, acid/base injection packages are used for membrane cleaning (CIP) and necessary disinfectants.
Pipes, Frame, and Auxiliary Equipment: Pressure vessels (high-pressure membrane housings), electrical panels, water storage tanks, and other auxiliary parts complete the RO system.
Applications of Industrial RO Systems in Various Industries
Industrial desalination systems have widespread applications across different industries. Examples include:
Food and Beverage Industry: Used in production lines of dairy, soft drinks, mineral water, and beverage factories. RO improves product quality and removes unwanted salts.
Pharmaceutical, Medical, and Healthcare Industries: Produces pure water for drug manufacturing, pharmaceutical consumables, and vaccine filling. RO water is nearly free of bacteria and organic materials, meeting pharmaceutical standards.
Boiler Feedwater and Power Plants: Provides clean feed water for steam boilers and turbines, removing suspended solids and dissolved salts to increase equipment lifespan and efficiency.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry: Produces ultra-pure water (DI water) for semiconductor and electronic board manufacturing. These industries require water free from any impurities, and RO can remove up to 98% of contaminants.
Agriculture (Greenhouses and Livestock): Supplies treated water for irrigation of salt-sensitive plants and clean drinking water for livestock. Removing salts and pollutants increases agricultural yields.
Metallurgy and Petrochemical Industries: Provides pure water for cooling and sensitive industrial processes; removes impurities from feed water in refineries and petrochemical plants.
Brackish and Seawater Desalination: Special RO units with higher operating pressures are designed for desalinating brackish and seawater (high TDS).
Industrial desalination unit being installed in a factory. RO systems are used in various industries including production lines and power plants.
Technical, Economic, and Environmental Advantages of Using RO
Technical:
The RO system is scalable and has no fixed capacity limit. It can treat brackish and even seawater, producing very high-quality water. The high precision in removing dissolved particles and microorganisms (up to >98%) and the use of membrane technology make RO one of the most accurate water treatment methods. Additionally, if a membrane fails, it can be replaced without shutting down the entire system.
Economic:
Energy consumption in RO is lower compared to thermal methods (distillation). RO systems have low maintenance costs and, due to minimal chemical usage (compared to ion-exchange resins), operational expenses are more economical. Quick installation and commissioning, ease of use, and adaptability to changes in feed water quality are other economic benefits of this method.
Environmental:
RO systems produce no secondary pollution except brine wastewater. Unlike ion-exchange or distillation methods that require chemicals, RO does not generate harmful new waste. Also, because it operates at normal temperatures, it avoids corrosion and thermal pollution issues. Therefore, using RO significantly helps conserve water resources and reduce environmental pollution.
Difference Between Industrial Reverse Osmosis and Other Water Treatment Methods
Comparison with Ultrafiltration (UF) and Nanofiltration (NF): RO has smaller pores and can remove dissolved solids and ions, whereas UF and NF only remove suspended particles and some large molecules. RO systems separate all dissolved salts.
Comparison with UV Treatment: UV systems are used solely for disinfection (eliminating bacteria and viruses) and cannot remove dissolved salts. In contrast, RO removes microbes as well and improves water quality to a potable level.
Comparison with Thermal Methods (Distillation): Thermal treatment consumes high energy. RO operates at normal temperature and pressure, resulting in much lower energy consumption. Also, distillation systems often face corrosion and scaling problems, which are less common in RO systems.
Comparison with Ion Exchange: Ion exchange resins only absorb specific ions (e.g., water hardness) and require chemical regeneration. RO removes a broader range of contaminants and is less sensitive to changes in feed water quality. Additionally, in RO systems, membranes can be replaced individually without stopping the entire process if needed.
What is a Deionizer?
How to Choose the Right Industrial Desalination System Based on Your Needs
To select an industrial water desalination system that fits your needs, consider the following parameters:
Capacity and Output Quality: First, determine the daily volume of treated water you require and the desired final quality (TDS and salinity). This will determine the number of membranes and pump power needed.
Feed Water Quality: Analyze the “feed water” entering the system. Parameters such as TDS, total hardness (ppm), free chlorine, iron, and other contaminants should be evaluated. For example, if water hardness exceeds 1000 ppm, pretreatment like resin softening or antiscalant injection is necessary. Salinity levels are generally classified into three groups: <8000, 8000–15000, or >15000 mg/L TDS, which determines the type of membrane required.
Specific Contaminants: If hazardous contaminants like arsenic, lead, or silica are present in the feed water, special filters (e.g., arsenic removal filters) and dedicated pretreatment systems must be added. Any unusual water analysis should be accounted for in the system design.
Space and Installation Constraints: Adjust the equipment size according to the available installation space. Pre-fabricated containerized or skid-mounted packages are available for quick installation. In remote locations, solar-powered or portable desalination units can be designed.
Costs: Finally, consider both the initial investment and operational costs. For instance, high feed water hardness or reduced membrane lifespan can increase maintenance expenses.
Maintenance and After-Sales Services
Periodic Membrane Cleaning and Regeneration: To extend membrane life, regular cleaning is performed using backwash (reverse flushing) and chemical cleaning (acid or alkali). This process typically occurs after several thousand hours of operation or based on flow reduction analysis.
Replacement of Pretreatment Filters: Sand, carbon, and cartridge filters should be replaced or serviced depending on feed water contamination (e.g., every 3–6 months) to prevent membrane fouling and damage.
Periodic Inspection: Pressure gauges, flow meters, and instrumentation devices must be calibrated regularly. Any unusual fluctuations in pressure or water quality should be promptly addressed.
Membranes: Membrane lifespan varies between 3 to 7 years depending on operating conditions (water quality and fouling level). After this period, membranes should be replaced to maintain system efficiency. It is recommended to always keep a spare membrane available.
Pumps and Mechanical Parts: Greasing and servicing of high-pressure pumps should be done periodically (e.g., annually). Any leakage, scratches, or damage to pressure vessels must be repaired immediately.
After-Sales Service: The Pardis Sadrab Caspian Purification Company provides operator training, 24/7 technical support, and supply of original spare parts. Maintenance packages are also available to ensure the system remains in optimal condition.
Comparison of Industrial Water Treatment Technologies
| Treatment Method | Removal of Dissolved Solids | Removal of Microorganisms | Energy Consumption | Maintenance Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) | Removes >98% of dissolved solids | Complete removal of bacteria and viruses | Medium energy (less than distillation) | Low maintenance (optimized with pretreatment) | Requires proper pretreatment to prevent membrane fouling |
| Distillation (Thermal) | 100% removal of dissolved solids (pure water) | Complete removal of impurities | Very high | High (scaling and corrosion) | Produces completely pure water; very high energy consumption |
| Ion Exchange (Resin) | Removes specific ions (water hardness) | ❌ Does not remove microorganisms | Low | Medium (chemical regeneration) | Suitable for hardness reduction; produces chemical waste |
| Ultrafiltration (UF) | Removes suspended particles and colloids | Removes bacteria and viruses | Low | Low (cartridge replacement) | Larger pores; dissolved solids pass through |
| UV Filter (Ultraviolet) | ❌ Does not remove dissolved solids | Removes bacteria and viruses | Very low | Very low | Only disinfects; effective for viruses and bacteria; does not remove chlorine or scale |
Conclusion
To choose and purchase the best industrial water desalination system tailored to your needs, contact the experts at Palayesh SadrAb Caspian. We offer free consultation and, after assessing your water conditions and requirements, recommend the most suitable solution. For price inquiries and specialized guidance, please contact the company’s sales office or fill out the consultation request form. Pure water is the capital of your industry — desalinate safely and efficiently with us!
FAQ
It is an advanced membrane system used to reduce water salinity and remove impurities. Raw water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane, which separates most of the dissolved solids. Industrial RO systems are used in various industries for boiler feed water, drinking water production, and water purification.
Yes, industrial reverse osmosis (RO) membranes are capable of completely removing heavy metals, dissolved minerals, and even some organic compounds. In fact, due to its very fine pores, RO retains almost all impurities on one side.
Yes. The pores of the RO membrane are smaller than viruses and bacteria, so the reverse osmosis (RO) process leads to their separation and removal. As a result, the effluent water will be microbially safe.
The RO method has a broader ability to remove pollutants compared to other physical and chemical methods. For example, the UV system only eliminates microorganisms and does not remove ions. Additionally, RO has lower energy consumption compared to thermal methods (like distillation) and, compared to ion exchange, is less dependent on the quality of the input water and chemicals. A summary of the differences is provided in the table above.
Yes. To prevent membrane clogging, a pre-treatment unit (such as a sand filter and activated carbon filter) is required. After several thousand hours of operation, the filters and membranes should be cleaned using backwashing and chemical CIP (Clean-In-Place) methods. This prevents performance decline and extends the membrane’s lifespan.
Typically, it ranges from 3 to 7 years (depending on the quality of the feed water and maintenance). If efficiency decreases, the faulty membrane can be easily removed and replaced with a new one, without needing to replace the entire system.
It depends on the system design and operating pressure. Typically, about 50–80% of the input water is produced as pure water (permeate), with the remainder discharged as brine wastewater. Proper engineering design can optimize this ratio.